We are currently witnessing wildlife loss at an alarming rate. According to the recent WWF Living Planet Report (2022), species populations have declined 69% on average in the last 50 years.[1]
Why are wild animals and plants in serious decline?
In short, the increasing demand for animal products has led to our current food system – so it’s largely due to the way we eat…
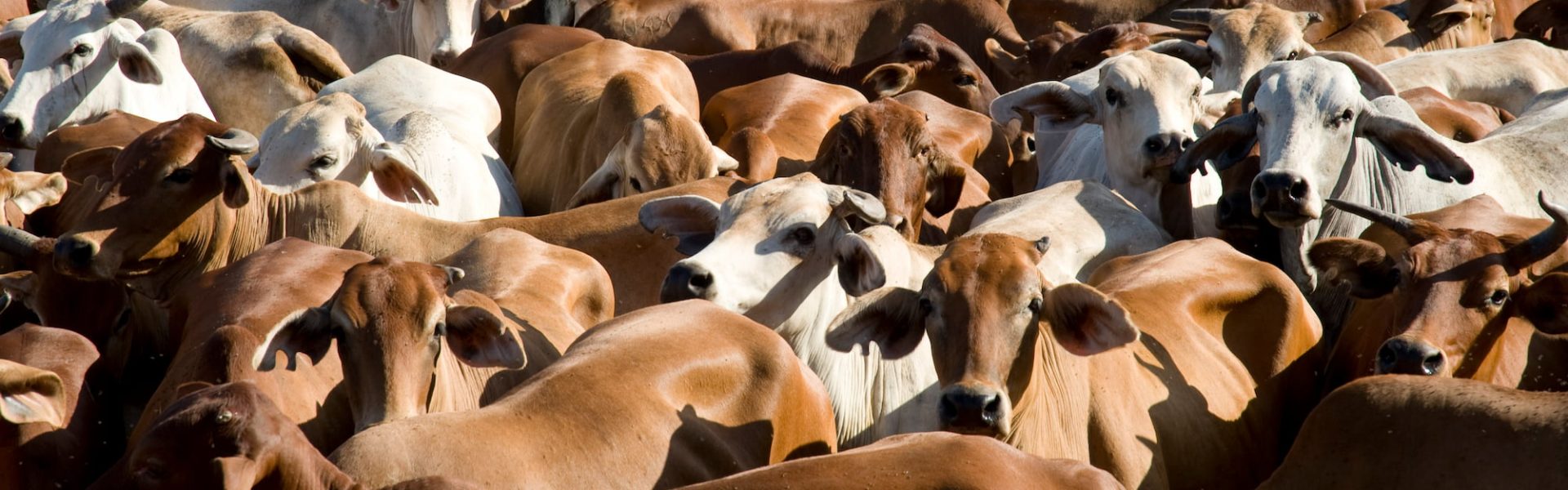
Across almost all categories of plants and animals, the leading cause of extinction is habitat destruction due to land clearing – and the vast majority of land clearing is to graze cattle for the beef and dairy industries, and to raise crops to feed farmed animals. Available data reveals that 41% of deforestation is due to pasture expansion for cattle, followed by 18% for soy and oilseeds – with most of that soy being fed to farmed animals (and a mere 6% of soy being eaten directly by humans).
For fish and other marine animals, the greatest extinction threat is exploitation, or in other words, fishing them to extinction.
The systems of ‘food production’ we inherited from those before us are having catastrophic impacts on animal species worldwide. And although we didn’t choose these food systems, we can change them.
We are the first generation that has a clear picture of the value of nature and the enormous impact we have on it. We may also be the last that can act to reverse this trend.
How did we get here? Over the last 100 years, the human population has essentially quadrupled. And as the population has grown, so too has the demand for resources, resulting in the mass clearing of forests, the suffering of billions of farmed animals each year, and the suffering of native animals who are losing their homes and food sources.
Land clearing isn’t an issue unique to the Amazon rainforest. It’s happening here in our own backyard, with thousands of hectares of forests being cleared by the beef industry in the last few years alone. Even if they manage to survive the destruction by bulldozers and other heavy machinery, koalas and other threatened and endangered native species are being left with less and less habitat.
This image contains content which some may find confronting
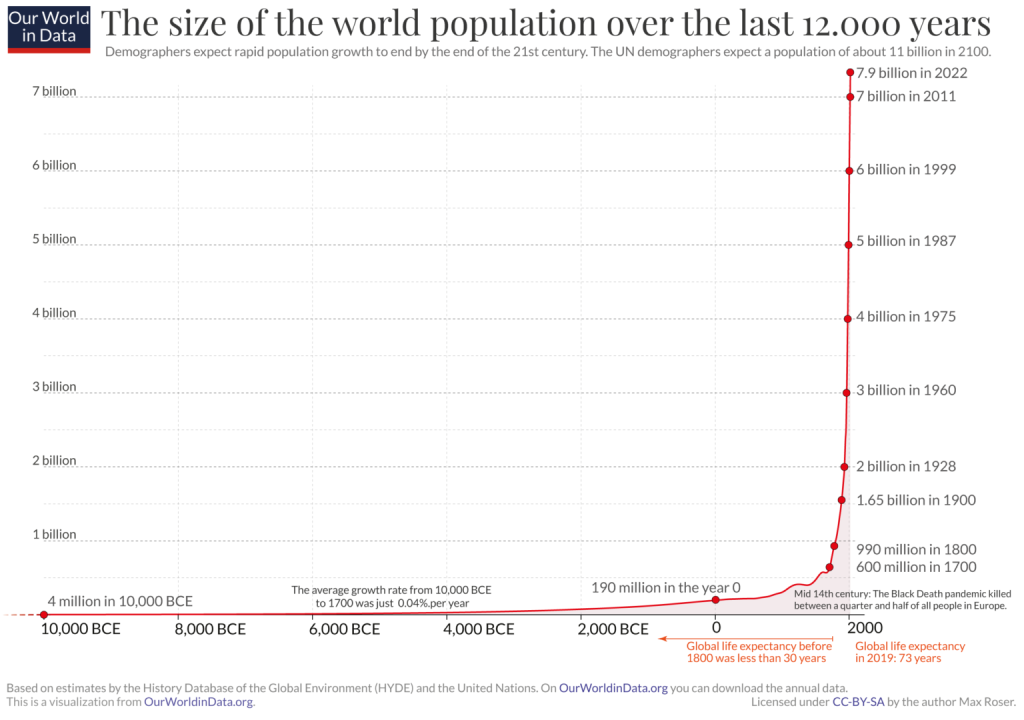
The human population has exploded in the last 100 years, and we urgently need to rethink our food systems to minimise our impact on animals and the planet. Filling our plates with more plants not only spares farmed animals from lives of deprivation and the terror of death in a slaughterhouse, but it is also the most sustainable way to eat. Graph source: Our World in Data.
Prior to this population explosion, the Earth’s resources were able to replenish more quickly than humans were using them. But now, consumer demand is putting a strain on the natural environment – the way we’re producing and eating food needs to shift.
Farmed land animals eat more food than they ‘produce’ for humans. In 2018, an estimated 69 billion chickens, 1.5 billion pigs, 574 million sheep and 302 million cattle were killed globally for meat production. So too were tens of billions of farmed fish. Each animal bred to be killed for their meat requires feed either from grazing or from crops, or both. It’s an inefficient system.
Importantly, of the billions of animals killed for human consumption each year, we must remember that each one of them is a sensitive and social individual too. Bred into a system that values them only for what they produce, farmed animals are often subjected to legalised cruelty, and are killed at just a fraction of their natural lifespan.
It is clear that we need to change the way we eat for animals and the planet… and fast.
Our survival depends on nature’s intricate ecosystems
Biodiversity maintains the world as we know it, which is another reason that the protection of all animals (regardless of what they look like) is so important. Nature’s ecosystems and the plants and animals that exist within them keep us alive. In one way or another, everything humanity needs to survive and thrive is provided by nature.
Many of the plant foods we eat rely on pollination from birds, bees and other insects. The destruction of natural habitat is a huge threat to bees and other pollinators, as they are rapidly losing areas for foraging and nesting. So too is the use of pesticides and other agricultural chemicals that are harmful to pollinators. Many plant-derived ingredients used in medical treatments also rely on pollination. The extinction of bees and other pollinating animals would pose a huge threat to our survival.
This image contains content which some may find confronting
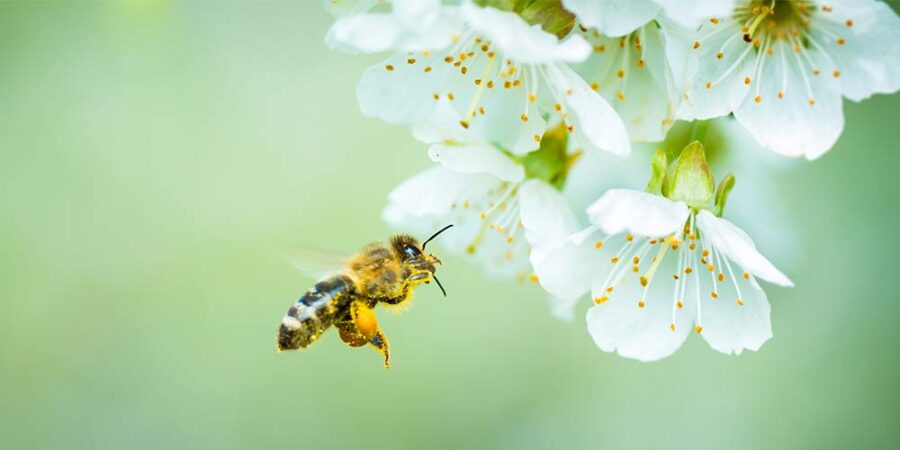

The destruction of forests is also linked to human-caused global warming. Trees absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but when swathes of forests are cleared, the stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere. Preserving and restoring forests and their ecosystems is therefore critical in mitigating our role in climate change.
Along with the physical benefits of forests, research increasingly shows that being in nature improves our psychological well-being as well. There’s no denying it – we need nature. And to conserve nature, we need to rethink what we put on our plates.
It’s not too late to shape a brighter future
There’s an ever-growing number of people choosing to help turn these trends around – with tasty and nutritious plants! Eating plant-based food is one of the simplest and most powerful ways to use our Earth’s resources more responsibly, and to protect wildlife in the process.
Research suggests that a shift to plant-based food could see global land use for agriculture reduced by 75% – and still feed the human population! Land that is currently used for farmed animals could be left to rest, eventually regenerating for wild animals and slowing human-caused global warming at the same time.
This image contains content which some may find confronting

Be the change you wish to see
As consumer demand has led to many of the issues we face today, it is consumer demand which can address these issues – by shifting demand to animal-friendly, and planet-friendly, alternatives.
If you would like to learn more about filling your plate with delicious, plant-rich food, order your free Veg Starter Kit today, or head to VegKit.com to browse resources and recipes.
References:
[1] WWF (2022) Living Planet Report 2022 – Building a naturepositive society. Almond, R.E.A., Grooten, M., Juffe Bignoli,
D. & Petersen, T. (Eds). WWF, Gland, Switzerland. (available at: https://wwflpr.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/lpr_2022_full_report.pdf)








